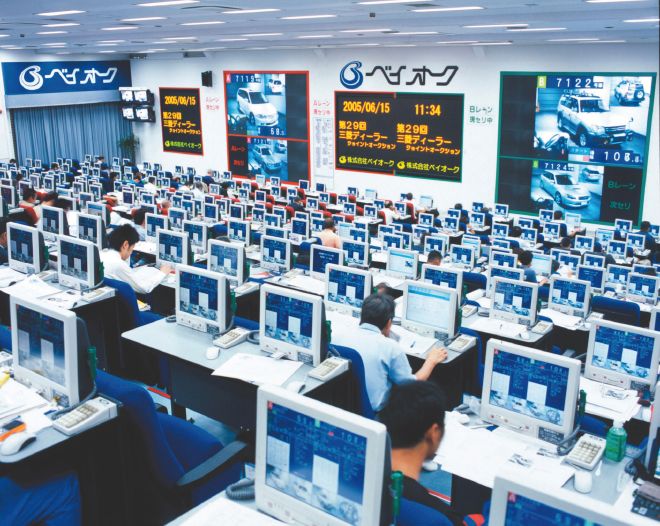
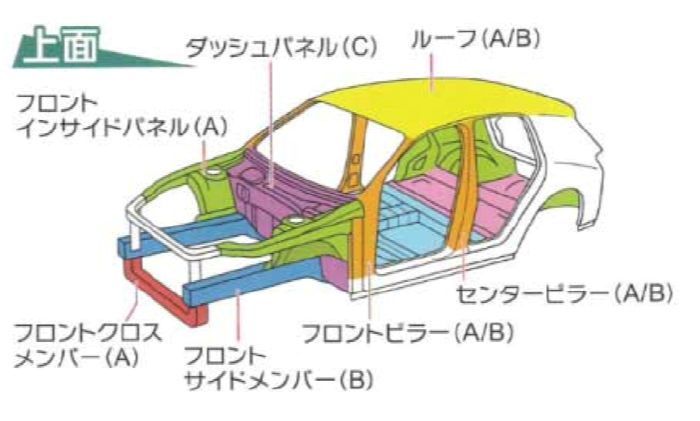
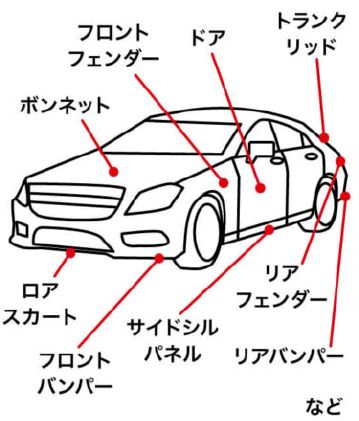
The first automobile auction was held in 1967 and was initially held irregularly as a manual bidding system.
Imagine the tuna or crab auctions at a fishing port.
The conductor and prospective buyers communicate using specialized "gestures" and "words" during the bidding.
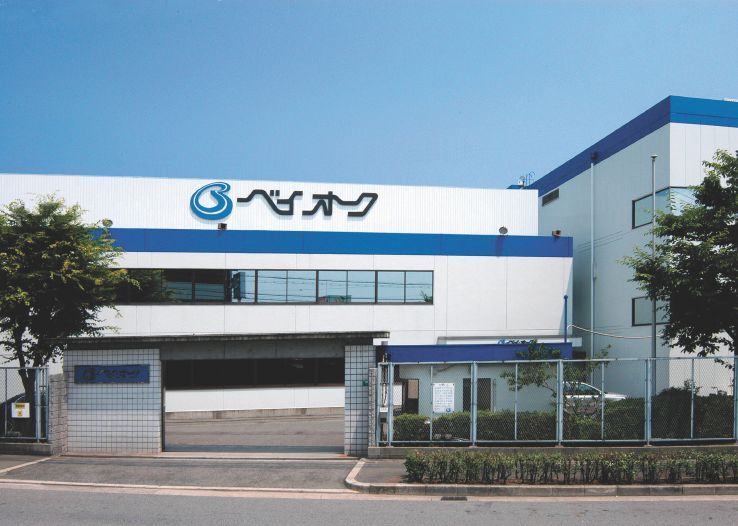
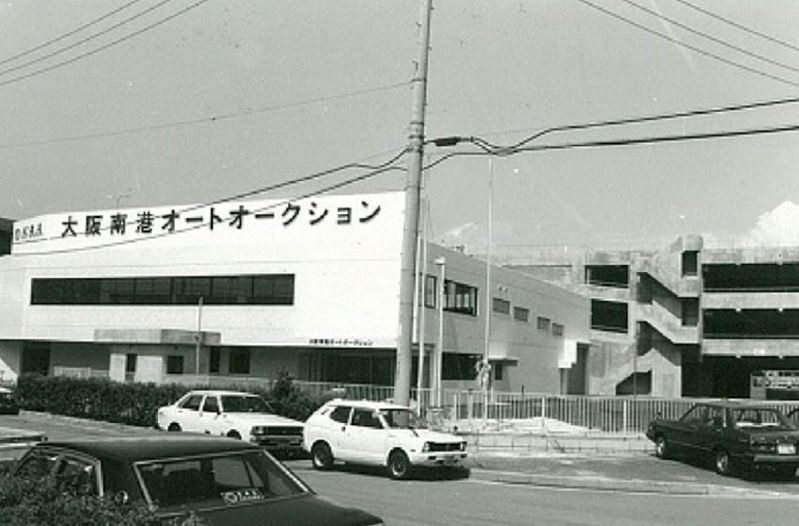
Bay auc (then the Osaka Nanko Used Car Cooperative) held its first auction in 1978. The photo on the left shows our company building at that time.
There was a lot of excitement with every successful bid.
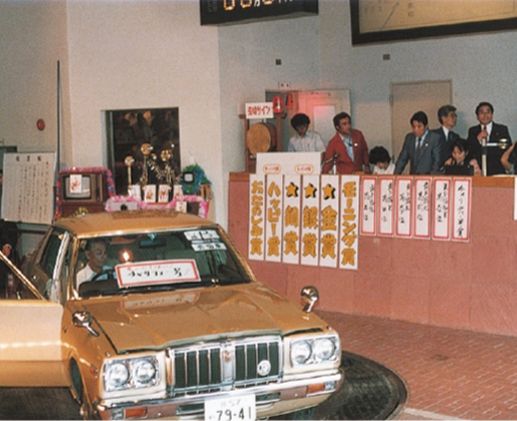

Manual bidding from 1978-84
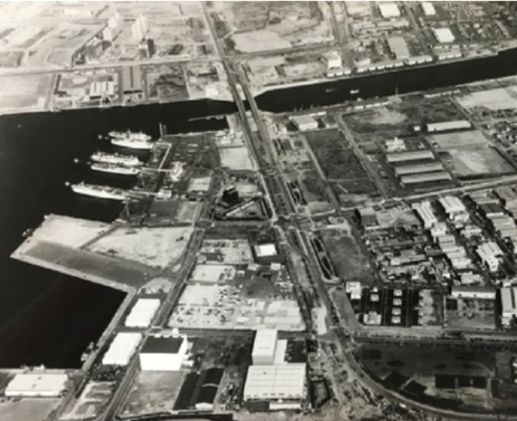

Aerial photo of Nanko around 1978
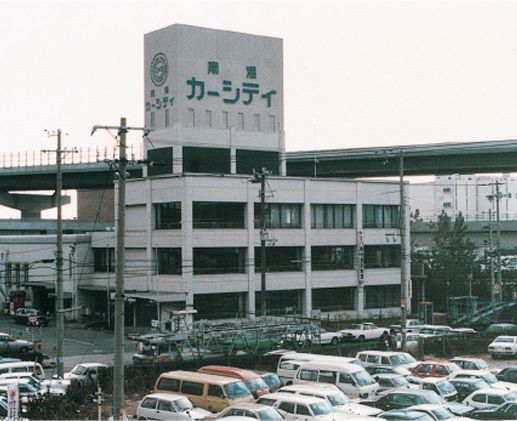

Around 1982, Nanko Car City was established, allowing more people to participate in the auction.
This photo, taken about four years after the previous one in 1984, shows the introduction of the POS system.
The exhibited vehicles are still conducted using the "**vehicle parading method**," where they pass in front of the bidding seats (hereafter, POS seats).
Bidding is done while physically observing the vehicle's movement, exhaust gas condition, color, etc.
As the number of listed vehicles increased with manual bidding, the processing capacity of the auctioneers became limited. Auctions took a long time from start to finish, and late at night, fatigue led to missed bid calls and disruptions in the bidding process.
For the bidders, too, since they could recognize the faces of other dealers who were bidding, friction with competitors arose, and there were problems where they were reluctant to bid on a desired car if a familiar dealer was competing.
Due to this background and technological innovation, the computer-based **POS system** was introduced.
Bay auc (then ONAA) built a new venue with the POS system and a multi-story parking garage north of the manual bidding venue, allowing more vehicles to be auctioned.
However, since the internet was not yet widespread, only those who came to the venue could participate in the bidding, and the number of attendees from all over West Japan increased year by year.
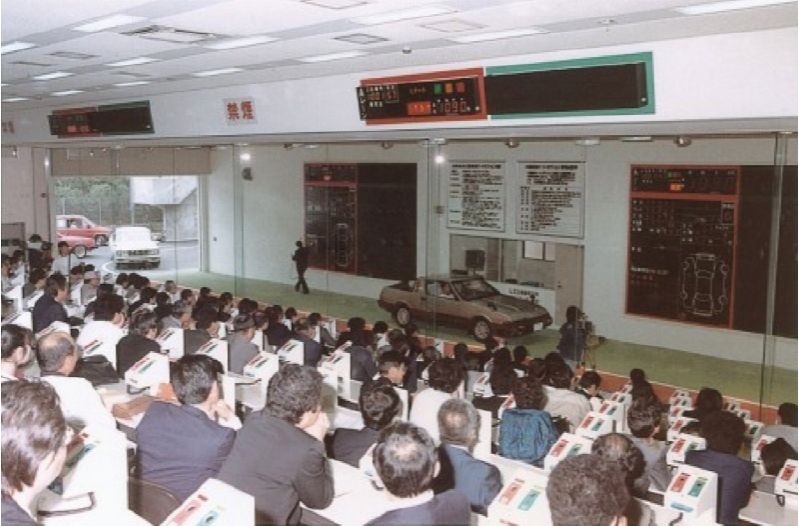


1984 POS system introduced, new venue established
Events in 1984
1/24 Takara can chu-hi launched
3/11 Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind released
3/18 Glico-Morinaga incident
5/1 Toyo Kogyo Co., Ltd. changed its name to Mazda Motor Corporation
11/1 New banknotes: 10,000 yen: Yukichi Fukuzawa; 5,000 yen: Inazo Nitobe; 1,000 yen: Soseki Natsume
About six more years passed.
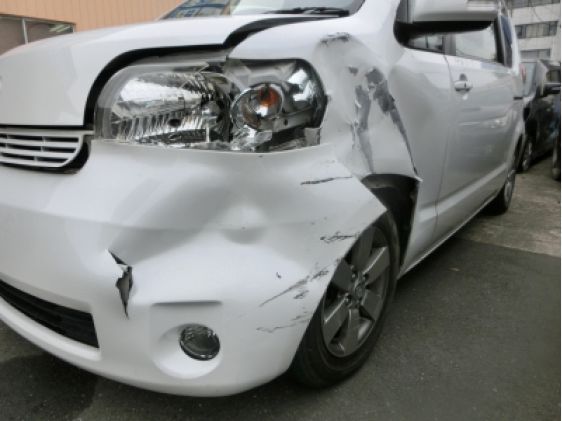
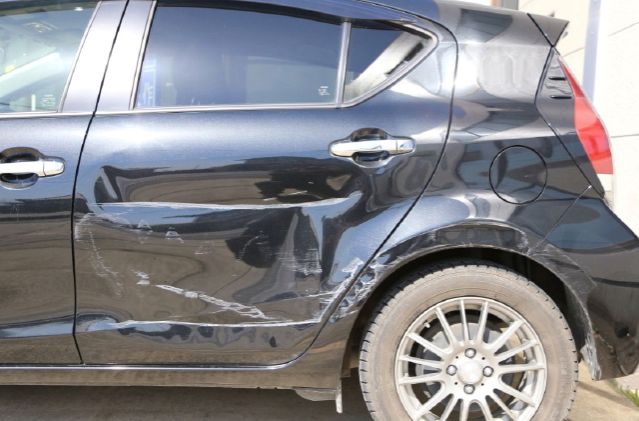
With the "vehicle parading method," if a vehicle had a problem, such as running out of gas or being immobile, the venue staff would have to push the car, disrupting the auction flow.
Furthermore, the internet was still not widespread, and the increase in registered members meant that the number of attendees exceeded the POS seats, making the expansion of POS seats an urgent need. However, some venues could not expand their POS seating due to the space required for parading vehicles.
Problems such as the shortage of POS seats, vehicles running out of gas, and contact or accidents between vehicles during parading within the venue were addressed by the development of video technology and the POS system. Exhibited cars were photographed in advance, and during the bidding, the images were displayed, allowing **two cars to be auctioned simultaneously**.
This shortened the time spent moving cars and reduced the need for manpower, significantly reducing the auction time.
However, since the internet was still not widespread at this point, the bidding was still limited to within the venue.
At Bay auc, traces of that era remain.
The main venue is designed like a theater so that parading vehicles could be seen, and there are vehicle entry/exit shutters behind the curtains on both sides at the front of the main venue.
To secure seating for attendees, POS seats were expanded onto the vehicle drive aisle and the second-floor lobby.
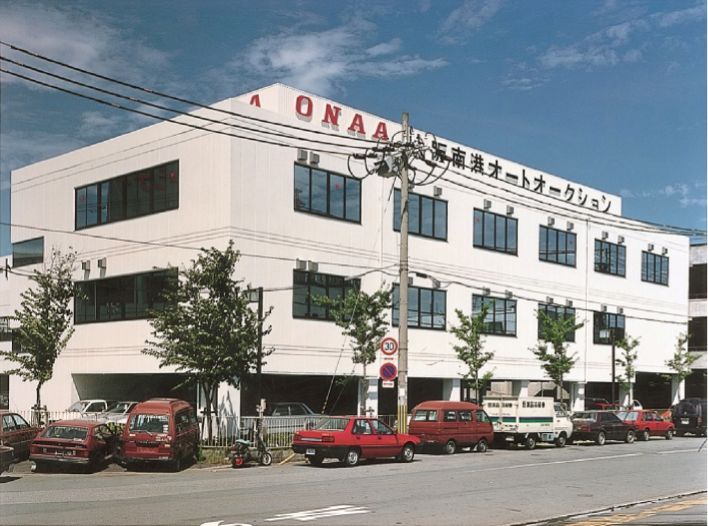

1992
Current administration building and sub-venue constructed. At the time, the 3rd floor was the cafeteria, and the 1st floor was the parking lot/passageway for the "vehicle parading method."
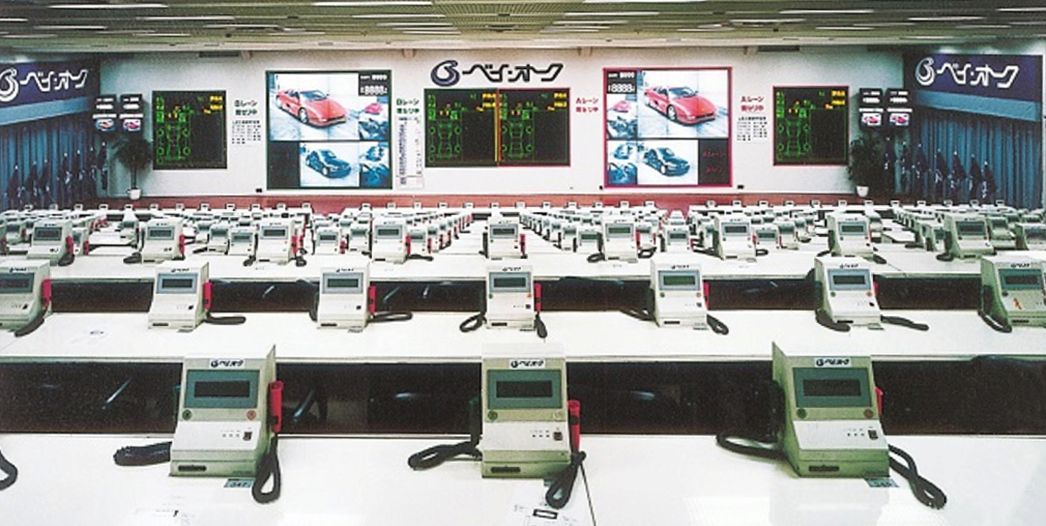

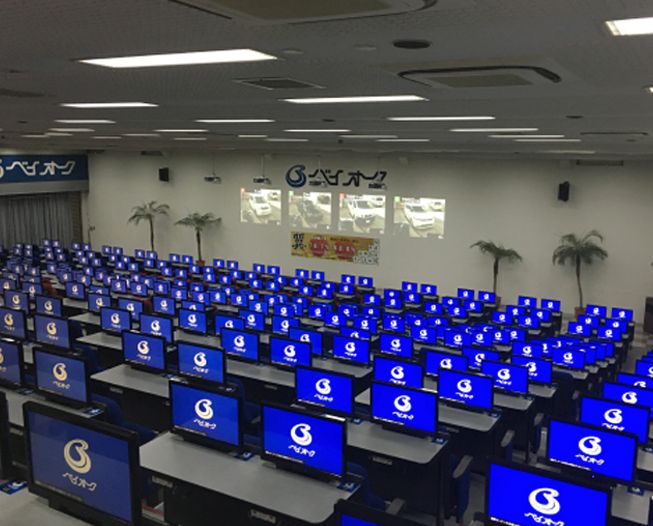
1998 Fully visual 2-lane auction (Photo from around 2000)
Events in 1998
2/7 Nagano Olympics opening
4/4 Antonio Inoki retired
4/5 Akashi Kaikyō Bridge opened
7/30 Obuchi Cabinet inaugurated
8/29 First iMac released
10/21 Game Boy released
With the spread of the internet in the 2000s, cooperation with other venues became possible, so Bay auc
worked hard to partner with many venues to allow people from all over Japan to successfully bid.
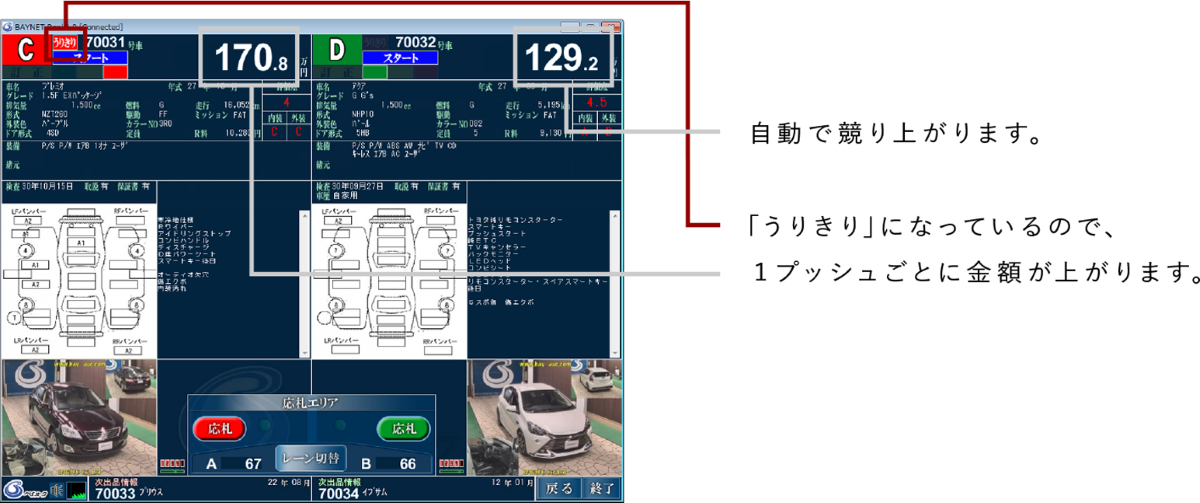
Initial online participation was limited to **bidding** (setting a desired maximum bid amount in advance), but with enhanced and stable communication,
**real-time bidding** became possible, increasing the number of people participating in the auction online without physically attending the venue.
2001 Real-time internet bidding started on Bay Net, our proprietary network.
2005 POS machines equipped with Bay Net were installed in all seats.
Events in 2001
4/2 Ichiro made his MLB debut in the US
4/26 First Koizumi Cabinet inaugurated
5/20 Japanese Wikipedia launched
9/11 September 11 attacks in the US
12/1 Birth of Princess Aiko